The Journey of Cotton: From Field to Factory
Cotton is a versatile and widely used natural fiber that has been cultivated for thousands of years. It is used in a variety of products, from clothing and household items to medical supplies and industrial materials. But have you ever wondered how this soft and fluffy fiber goes from being a plant in a field to a finished product in a factory? In this article, we will take a detailed look at the journey of cotton, from the field to the factory.
The process of turning cotton into a usable material begins in the fields. Cotton plants are typically grown in warm and humid climates, such as in the southern United States, India, and China. The plants are carefully tended to by farmers, who monitor their growth and protect them from pests and diseases. When the cotton bolls, or seed pods, are fully grown and burst open, it is time for harvesting.
Harvesting cotton is a labor-intensive process that involves picking the cotton bolls by hand or using a machine. Handpicking is the traditional method and is still used in many parts of the world. It involves workers walking through the fields and carefully picking the cotton bolls from the plants. This method ensures that only the ripe bolls are picked, resulting in higher quality cotton. However, it is a time-consuming and expensive process, which is why many farmers have switched to using machines.
Once the cotton has been harvested, it is transported to a cotton gin, where the seeds are removed from the fibers. The cotton gin is a machine that separates the seeds from the cotton fibers by using a series of rotating saws and brushes. This process is crucial as it not only separates the seeds but also removes any debris or impurities from the cotton.
After ginning, the cotton fibers are compressed into large bales and sent to textile mills for further processing. At the mill, the bales are opened and the fibers are cleaned and straightened. This process is known as carding and involves passing the fibers through a series of rollers with wire teeth that comb and align the fibers. The result is a thin and continuous strand of cotton called a sliver.
The sliver is then drawn, which involves stretching and thinning the fibers to make them stronger and more uniform. This process is repeated several times until the desired thickness is achieved. The drawn sliver is then spun into yarn, which is done by twisting the fibers together to create a strong and continuous thread. The yarn is then wound onto spools or cones, ready to be used in the next stage of the process.
The next step is weaving or knitting, where the yarn is turned into fabric. Weaving involves interlacing the yarns at right angles to create a woven fabric, while knitting involves looping the yarns together to create a knitted fabric. Both processes require specialized machines and skilled workers to create the desired fabric.
Once the fabric is woven or knitted, it is then dyed and finished. Dyeing involves adding color to the fabric using various techniques, such as immersion dyeing or printing. Finishing involves treating the fabric to improve its appearance, texture, and durability. This can include processes such as bleaching, softening, and adding a protective coating.
After finishing, the fabric is inspected for quality and then cut and sewn into various products, such as clothing, bedding, and towels. These products are then packaged and shipped to retailers or directly to consumers.
In conclusion, the journey of cotton from field to factory is a complex and fascinating process that involves many steps and skilled workers. From the careful cultivation of the cotton plant to the weaving and finishing of the fabric, each stage is crucial in creating the high-quality cotton products that we use every day. So the next time you put on a cotton shirt or use a cotton towel, take a moment to appreciate the journey that this humble fiber has taken to reach your hands.
Behind the Scenes: The Machinery Used in Cotton Processing
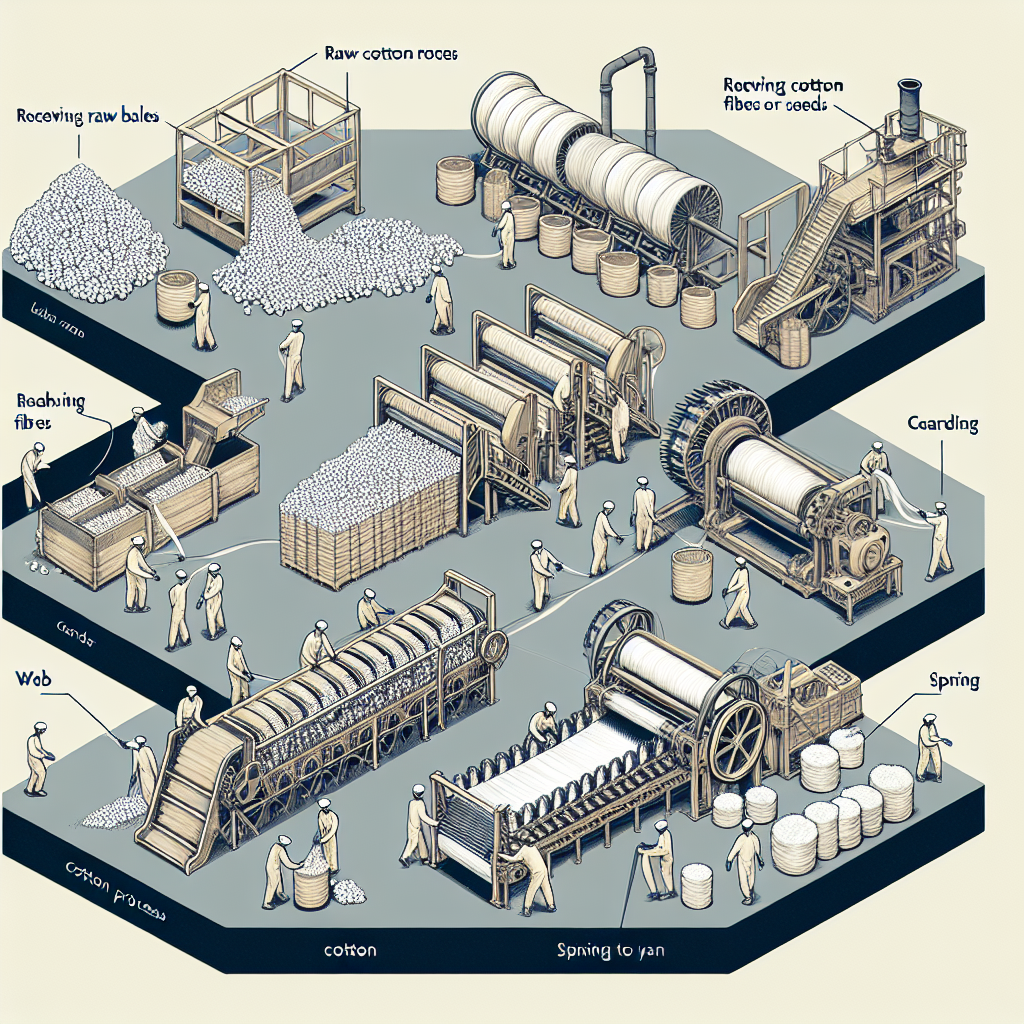
Cotton is a versatile and widely used material, found in everything from clothing to household items. But have you ever wondered how this soft and fluffy material is transformed from a plant into the fabric we know and love? The answer lies in the behind-the-scenes process of cotton processing in factories.
The journey of cotton processing begins in the fields, where the cotton plants are harvested and the raw cotton is collected. This raw cotton is then transported to factories, where it undergoes a series of steps to become the final product.
The first step in the cotton processing process is ginning. This is the process of separating the cotton fibers from the seeds and other debris. In the past, this was done by hand, but with the advancement of technology, ginning is now done using machines called cotton gins. These machines use rotating saws to remove the seeds and other impurities from the cotton fibers, leaving behind clean and fluffy cotton.
Once the cotton has been ginned, it is then sent to the next stage of processing, which is carding. This process involves combing the cotton fibers to align them in the same direction. This not only makes the fibers easier to spin, but it also ensures that the final product is of consistent quality. Carding machines use a series of rollers and brushes to comb the fibers, resulting in a thin sheet of cotton known as a sliver.
The next step in the process is spinning. This is where the cotton fibers are twisted together to form yarn. In the past, this was done using spinning wheels, but now it is done using spinning machines. These machines draw out the sliver and twist it into a continuous strand of yarn. The thickness of the yarn can be adjusted depending on the desired end product.
After spinning, the yarn is then sent to the weaving or knitting stage. Weaving is the process of interlacing the yarn to create a fabric, while knitting involves looping the yarn together to create a fabric. Both processes are done using specialized machines that can produce a variety of fabric types, from simple cotton sheets to intricate patterns.
Once the fabric has been woven or knitted, it is then sent to the finishing stage. This is where the fabric is treated to improve its appearance, texture, and durability. The fabric is first washed and bleached to remove any impurities and brighten the color. It is then dyed to achieve the desired color. After dyeing, the fabric is treated with chemicals to make it softer and more wrinkle-resistant. Finally, the fabric is dried and pressed to give it a smooth and finished look.
The machinery used in cotton processing is constantly evolving and improving, making the process more efficient and cost-effective. Modern factories use computer-controlled machines that can perform multiple tasks at once, resulting in a faster and more precise production process.
In addition to the machinery used in cotton processing, there are also various quality control measures in place to ensure that the final product meets the required standards. Samples of the fabric are regularly tested for strength, colorfastness, and other factors to ensure that the fabric is of high quality.
In conclusion, the process of cotton processing in factories involves a series of steps, each one crucial in transforming raw cotton into the fabric we know and love. From ginning to weaving, the machinery used in this process plays a vital role in producing high-quality cotton fabric. So the next time you put on your favorite cotton shirt or snuggle up in a soft cotton blanket, remember the intricate process that went into making it.
Sustainable Practices in Cotton Processing: A Look at Eco-Friendly Factories
Cotton is one of the most widely used natural fibers in the world, with a long history dating back to ancient civilizations. It is a versatile and durable material that is used in a variety of products, from clothing and bedding to medical supplies and industrial materials. However, the production of cotton has come under scrutiny in recent years due to its impact on the environment. The traditional methods of processing cotton in factories have been found to be harmful to the planet, leading to the rise of eco-friendly factories that prioritize sustainable practices.
The process of turning raw cotton into usable fabric involves several stages, each of which has the potential to cause harm to the environment. The first step is harvesting, where the cotton is picked from the fields and transported to the factories. In traditional factories, this transportation is often done using fossil fuel-powered vehicles, contributing to carbon emissions. However, eco-friendly factories have started using alternative modes of transportation such as electric vehicles or even bicycles, reducing their carbon footprint.
Once the cotton arrives at the factory, it goes through a process called ginning, where the seeds are removed from the fibers. This process generates a significant amount of waste, including the seeds, stems, and leaves of the cotton plant. In traditional factories, this waste is often burned, releasing harmful pollutants into the air. However, eco-friendly factories have found ways to repurpose this waste, turning it into biodegradable packaging materials or using it as a source of biofuel.
The next step in the process is spinning, where the cotton fibers are twisted together to form yarn. This process requires a significant amount of water, and traditional factories often use large amounts of freshwater, contributing to water scarcity in many regions. In contrast, eco-friendly factories have implemented water-saving techniques such as recycling and reusing water, as well as using rainwater harvesting systems. These practices not only reduce the factory’s water consumption but also help to conserve this precious resource.
After spinning, the yarn is then woven into fabric, which is then dyed and finished. The dyeing process is one of the most environmentally damaging stages in cotton processing, as it involves the use of toxic chemicals that can pollute water sources and harm workers’ health. Eco-friendly factories have turned to natural and organic dyes, which are made from plant-based materials and do not contain harmful chemicals. These dyes not only reduce the environmental impact but also provide a safer working environment for the factory workers.
In addition to using eco-friendly materials and techniques, sustainable factories also prioritize fair labor practices. Traditional cotton processing factories have been criticized for their use of child labor and poor working conditions. However, eco-friendly factories have strict policies in place to ensure fair wages and safe working conditions for their employees. They also prioritize the use of renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels.
The final stage in the process is packaging and transportation, where the finished cotton products are prepared for distribution. Traditional factories often use plastic packaging, which contributes to the growing problem of plastic pollution. In contrast, eco-friendly factories use biodegradable and compostable packaging materials, reducing their impact on the environment. They also prioritize using sustainable transportation methods, such as electric or hybrid vehicles, to reduce carbon emissions.
In conclusion, the production of cotton has a significant impact on the environment, but eco-friendly factories are leading the way in implementing sustainable practices. From transportation and waste management to water conservation and fair labor practices, these factories are making a conscious effort to reduce their environmental footprint. As consumers become more aware of the impact of their purchases, the demand for sustainable cotton products is on the rise. By supporting eco-friendly factories, we can contribute to a more sustainable future for the cotton industry and the planet as a whole.











